
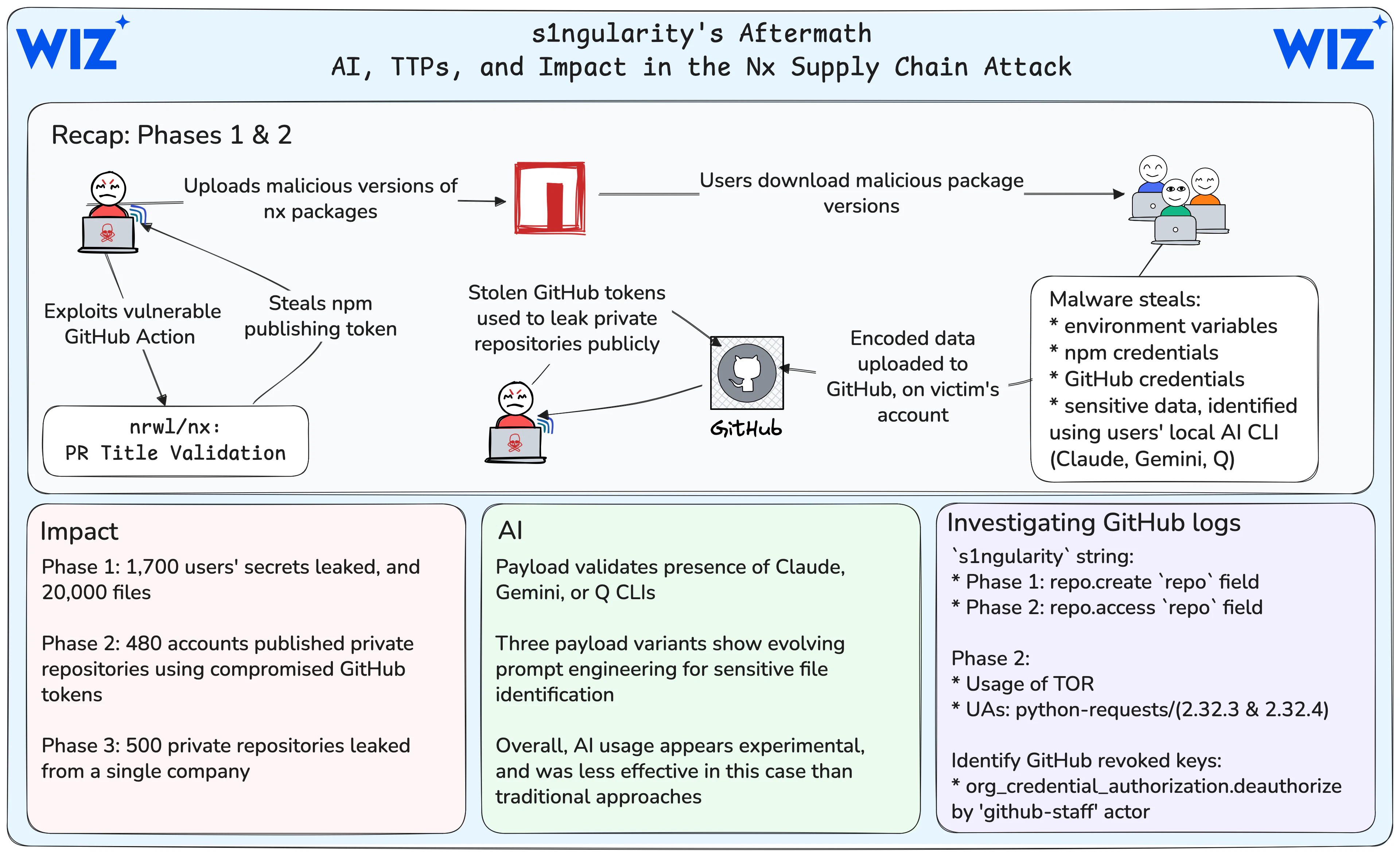
Unknown attackers weaponized artificial intelligence (AI) command-line tools to automatically hunt for sensitive data, compromising over 2,180 GitHub accounts in a sophisticated malware campaign targeting developers.
The attack began on August 26 when hackers exploited a security flaw in Nx, a popular development framework with 5.5 million weekly downloads. They hijacked the platform’s publishing system to distribute infected software packages across the npm registry.
The malware searched for AI programs already installed on victims’ machines. When it found Claude, Google Gemini, or Amazon Q command tools, it used them to scan for sensitive data.
This marked the first time hackers weaponized AI assistants in a major supply chain attack. The malware provided these AI tools with specific instructions to find passwords, crypto wallets, and secret keys.
The hackers refined their approach throughout the campaign. They evolved from basic file searches to sophisticated prompts designed to bypass AI safety systems.
“The evolution of the prompt shows the attacker exploring prompt tuning rapidly throughout the attack,” Wiz Research found.
However, the AI-powered method proved inconsistent. Roughly 75% of attempts failed due to missing tools, task refusals by AI models, or configuration problems.
The attack unfolded across three distinct phases over six days. In the first wave, attackers directly compromised 1,700 users and leaked over 2,000 verified secrets. They also extracted 20,000 files from infected systems.
GitHub removed the malicious repositories after eight hours. However, attackers had already copied the stolen information.
The second wave caused more damage. Between August 28 and 29, hackers used stolen login credentials to flip private repositories public. This exposed 480 more accounts and 6,700 private projects.
The final phase targeted a single organization starting August 31, resulting in 500 additional leaked repositories.
Source: Wiz Research
The attack exploited multiple security weaknesses in Nx’s publishing system. Attackers used a vulnerable GitHub Actions workflow that allowed external contributors to run code with elevated permissions.
“Retrospectively, we made one critical mistake: if you gained access to our trusted environment, you were able to publish to NPM,” Nx developers wrote in their post-incident analysis.
The company has since added stronger security measures. This includes trusted publisher authentication and manual approval requirements for all package releases.
Security researchers warn that the damage could continue growing. Nearly 40% of leaked npm tokens and 5% of GitHub tokens still worked days after the attack, creating opportunities for follow-up attacks.
The incident represents a concerning evolution in supply chain attacks, demonstrating how hackers are adapting AI tools originally designed for legitimate development work into sophisticated data-stealing weapons.
Organizations should check their GitHub logs for suspicious “s1ngularity” activity and change any compromised passwords immediately.


















